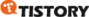if object_id ( 'tblx') is not null
drop table tblx
go
select
c1, c2, c3, isnull(sign(c3-lag(c3, 1) over (partition by c1 order by (c2))),0) c4
into tblx
from
(
select char(a.idx % 26 + 65) c1
, cast ('20180101' as datetime) + b.idx c2
, cast(abs(checksum(newid())) % 100000 as int) c3
from
(
select top 26 cast(row_number() over (order by (select 1)) as int) -1 idx
from sys.objects a1
) a,
(
select top 365 cast(row_number() over (order by (select 1)) as int) -1 idx
from sys.objects a1
, sys.objects a2
) b
) a
where
datepart(weekday, c2 ) not in (1,7)
--
select * from tblx
-- 1
; with a as
(
select row_number() over ( partition by c1, c order by c2) rn
, *
from tblx
,
(
select 0 c union all
select 1 union all
select 2 union all
select 3 union all
select 4 union all
select 5
) b
)
select
max(c1) c1, min(c2) c2
, max(case when c = 0 then c3 else null end ) d0
, max(case when c = 1 then c3 else null end ) d1
, max(case when c = 2 then c3 else null end ) d2
, max(case when c = 3 then c3 else null end ) d3
, max(case when c = 4 then c3 else null end ) d4
, max(case when c = 5 then c3 else null end ) d5
from a
group by c1, rn-c
having max(case when c = 0 then c3 else null end ) is not null
and sign (max(case when c = 1 then c3 else null end ) - max(case when c = 0 then c3 else null end ))
+ sign (max(case when c = 2 then c3 else null end ) - max(case when c = 1 then c3 else null end ))
+ sign (max(case when c = 3 then c3 else null end ) - max(case when c = 2 then c3 else null end ))
+ sign (max(case when c = 4 then c3 else null end ) - max(case when c = 3 then c3 else null end ))
+ sign (max(case when c = 5 then c3 else null end ) - max(case when c = 4 then c3 else null end ))
= 5
order by c1, c2
-- 2
; with a
as
(
select *
, lag(c3, 1) over (partition by c1 order by (c2)) dm1
, lag(c3, 2) over (partition by c1 order by (c2)) dm2
, lag(c3, 3) over (partition by c1 order by (c2)) dm3
, lag(c3, 4) over (partition by c1 order by (c2)) dm4
, lag(c3, 5) over (partition by c1 order by (c2)) dm5
from tblx
)
select *
from a
where
sign(dm4-dm5)
+ sign(dm3-dm4)
+ sign(dm2-dm3)
+ sign(dm1-dm2)
+ sign(c3-dm1) = 5
-- 3
select a.c1, a.c2, a.c3
from
(
select a.* , count(*) over (partition by c1, rn2) as cn
from
(
select a.*
, row_number() over (partition by c1 order by c2)
- row_number() over (partition by c1, c4 order by c2) as rn2
from tblx a
) a
where c4 = 1
) a
where cn >= 5
order by c1, c2