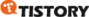Deadlock은 Mutual Exclusion, Hold and Wait, No Preemption, Circular Wait 조건이 모두 만족될 때 발생.
예를 들어, 단일 PK를 가진 테이블에서의 삭제 쿼리와, attachid가 없는 인덱스를 대상으로 하는 UPDATE 구문이 deadlock발생. 이를 해결하기 위해 Two Step 업데이트를 활용.
Two Step 업데이트는 단일 PK를 이용한 단건 삭제와 유사한 방식으로 동작하며, 핵심은 실제 업데이트 대상만을 선별하여 순차적으로 처리할 수 있도록 하는 것에 있다. 이를 통해 deadlock 발생 가능성을 최소화할 수 있음. 사실 View Select 구문에 NOLOCK 보다 UDLOCK 을 거는게 더 좋을수 있다. 그런데, 더이상 deadlock 이 안생기니 그만 보는것으로...
-- 기존 쿼리
(@P0 nvarchar(4000),@P1 int,@P2 int)
update ai set ai.openyn = @P0
from dbo.CLT_a ai with (index(PK_CLT_a))
where ai.clubid = @P1
and ai.articleid = @P2
and ai.attachtype = 'I';
-- 기존 쿼리 DESC
/*
attachid 조건이 없어서 articleid 범위를 훑으며 여러 row에 lock
다른 세션과 락 획득 순서 엇갈림
deadlock.
*/
-- 개선쿼리
declare @p0 char(1) = 'N'
, @p1 int = 10000006
, @p2 int = 8
update t
set t.openyn = @P0
from
(
select top 100 percent clubid, articleid, attachid
from dbo.CLT_a with (nolock, index(idx3_CLT_a_ROS))
where clubid=@P1 and articleid=@P2 and attachtype='I'
order by clubid, articleid desc, attachid
) a
inner loop join CLT_a t
on a.clubid = t.clubid
and a.articleid = t.articleid
and a.attachid = t.attachid
-- 개선 쿼리 DESC
-- two step 업데이트로 항상 PK 단일 행에 대한 업데이트 진행
-- Mutual exclusion, Hold and wait, No preemption, Circular wait 에서 Circular wait 조건을 제거해 deadlock을 방지한다.
-- loop join을 강제해 순서를 유지한 update가 되도록 한다.
idx3_CLT_a_ROS nonclustered located on PRIMARY clubid, attachtype, articleid -- view 에서 사용하는 index
PK_CLT_a clustered, unique, primary key located on PRIMARY clubid, articleid(-), attachid -- pk update